How to operate a drone safely and effectively is a skill that opens up exciting possibilities, from breathtaking aerial photography to efficient surveying. This guide provides a structured approach, covering everything from understanding basic components and pre-flight checks to mastering flight controls and advanced maneuvers. We’ll explore essential safety procedures, legal regulations, and practical troubleshooting tips, empowering you to confidently navigate the skies with your drone.
Whether you’re a novice eager to take your first flight or an experienced pilot looking to refine your techniques, this comprehensive resource offers valuable insights and practical advice. We will delve into the intricacies of drone technology, providing clear explanations and step-by-step instructions to help you achieve optimal performance and stunning results. Get ready to unlock the full potential of your drone!
Drone Components and Terminology
Understanding the various components of a drone and the associated terminology is crucial for safe and effective operation. This section will detail the function of each major component and provide a glossary of common terms.
Drone Component Functions
A drone’s functionality relies on the interplay of several key components. Each plays a vital role in its flight and image capture capabilities.
- Propellers: These rotating blades generate the thrust necessary for lift and maneuverability. Different propeller designs offer varying levels of thrust and efficiency.
- Motors: Electric motors power the propellers, converting electrical energy into rotational motion. Motor performance directly impacts flight speed, stability, and battery life.
- Flight Controller: The “brain” of the drone, this unit processes data from various sensors (gyroscopes, accelerometers, etc.) to maintain stability and execute pilot commands. It’s responsible for maintaining altitude, orientation, and overall flight stability.
- Battery: Provides the power source for all drone components. Battery capacity and type significantly affect flight time and performance. Different battery chemistries offer various advantages and disadvantages.
- GPS (Global Positioning System): Enables precise positioning and navigation. GPS data allows for features like autonomous flight modes, return-to-home functionality, and geofencing.
- Camera: Captures aerial photos and videos. Camera specifications such as resolution, sensor size, and lens type determine image quality.
Drone Terminology Glossary
Familiarizing yourself with common drone terminology will enhance your understanding of drone operation and maintenance.
- LiPo (Lithium Polymer): A common type of rechargeable battery used in drones, known for its high energy density.
- LiHV (Lithium Polymer High Voltage): A variation of LiPo batteries with a higher voltage, offering increased power and flight time.
- ESC (Electronic Speed Controller): Regulates the speed of the motors, allowing for precise control of thrust.
- IMU (Inertial Measurement Unit): A sensor system that measures the drone’s orientation and movement.
- RTF (Ready-To-Fly): Drones that come fully assembled and ready for immediate use.
- FPV (First-Person View): A system that allows the pilot to see what the drone’s camera sees, providing a real-time perspective during flight.
- Gimbal: A stabilized mounting system for the camera, minimizing image shake and ensuring smooth footage.
- Geofencing: Setting virtual boundaries that restrict the drone’s flight area.
Drone Battery Comparison
Different battery types offer varying performance characteristics. The choice of battery impacts flight time and overall drone performance.
| Battery Type | Voltage (V) | Capacity (mAh) | Approximate Flight Time (minutes) |
|---|---|---|---|
| LiPo 3S | 11.1 | 1300 | 15-20 |
| LiPo 4S | 14.8 | 1500 | 20-25 |
| LiHV 3S | 12.6 | 1300 | 18-22 |
| LiHV 4S | 16.8 | 1500 | 25-30 |
Pre-Flight Checklist and Safety Procedures
A thorough pre-flight checklist is essential for ensuring safe and responsible drone operation. This section details the steps involved in a safe pre-flight inspection and highlights best practices for hazard identification and avoidance.
Pre-Flight Checklist
Before each flight, perform a comprehensive inspection to identify and address any potential issues. This ensures safe and reliable drone operation.
- Inspect propellers for damage or cracks.
- Check battery levels and ensure proper connection.
- Verify GPS signal strength and satellite lock.
- Confirm camera settings and functionality.
- Check flight controller for any error messages.
- Review weather conditions and airspace restrictions.
- Identify and avoid potential hazards such as obstacles, people, and animals.
- Ensure all necessary permits and licenses are in order.
Hazard Identification and Avoidance
Successful drone operation requires awareness of potential hazards and the ability to mitigate risks. Understanding these factors ensures both safety and legal compliance.
- Obstacles: Trees, buildings, power lines, and other objects can cause collisions. Maintain a safe distance and plan your flight path accordingly.
- Weather: Strong winds, rain, and fog can significantly impact drone stability and control. Avoid flying in adverse weather conditions.
- Airspace Restrictions: Restricted airspace includes airports, military bases, and other areas where drone operation may be prohibited. Always check for airspace restrictions before flying.
Safe Pre-Flight Inspection Flowchart
A visual representation of the pre-flight inspection process can help ensure all steps are completed consistently.
1. Inspect Propellers → 2. Check Battery → 3. Verify GPS Signal → 4. Confirm Camera Settings → 5.
Check Flight Controller → 6. Review Weather & Airspace → 7. Identify Hazards → 8. Verify Permits/Licenses → Proceed to Flight
Taking Off and Landing
Safe takeoff and landing procedures are critical for preventing accidents and damage. This section details the steps involved in a safe takeoff and landing, including emergency procedures.
Safe Takeoff and Landing Procedure, How to operate a drone
A smooth and controlled takeoff and landing is essential for safe drone operation. These steps should be followed consistently for each flight.
- Position the drone on a level surface, away from obstacles.
- Power on the drone and controller.
- Wait for GPS signal acquisition (if applicable).
- Slowly increase throttle to initiate takeoff.
- Maintain a steady ascent to a safe altitude.
- For landing, gradually decrease throttle and gently lower the drone to the ground.
- Power off the drone and controller.
Emergency Landing Procedure
In case of unforeseen circumstances, a swift and controlled emergency landing is crucial. Knowing these steps can prevent damage and potential injury.
- Immediately reduce throttle to initiate descent.
- Attempt to regain control, if possible.
- Select the nearest safe landing zone.
- Execute a controlled descent, prioritizing safety.
- After landing, assess the drone for damage.
Takeoff and Landing Techniques
Different drone models may have slightly different takeoff and landing procedures. Understanding these variations ensures safe and efficient operation.
Some drones offer automated takeoff and landing features, simplifying the process. Others may require more manual control. Always refer to your drone’s specific manual for detailed instructions.
Basic Flight Controls and Maneuvers
Understanding the function of each flight control stick is essential for basic drone maneuvers. This section explains the relationship between stick inputs and drone movement.
Flight Control Stick Functions
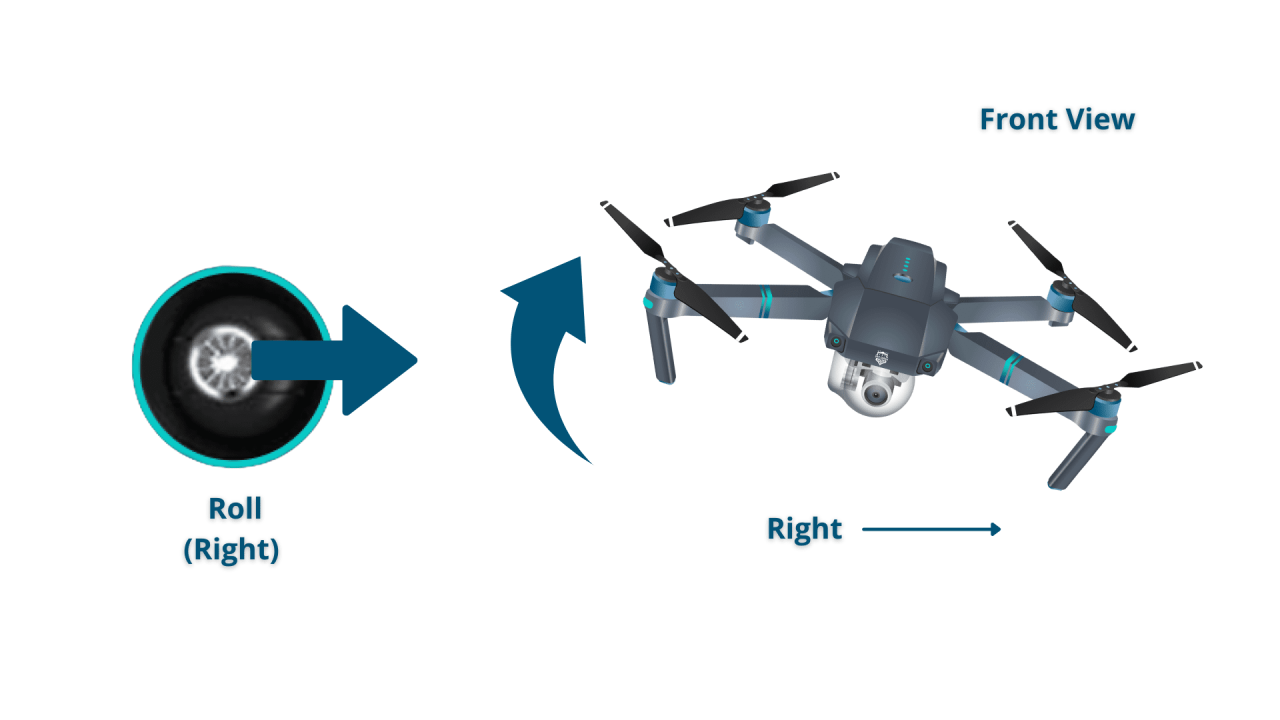
The control sticks on a drone remote typically control pitch, roll, yaw, and throttle.
- Pitch: Controls movement forward and backward.
- Roll: Controls movement left and right.
- Yaw: Controls rotation around the vertical axis.
- Throttle: Controls altitude (ascending and descending).
Basic Flight Maneuvers
Mastering these basic maneuvers is fundamental to safe and effective drone piloting.
- Hovering: Maintaining a stable position in the air.
- Ascending: Increasing altitude.
- Descending: Decreasing altitude.
- Turning: Rotating the drone around its vertical axis.
Stick Inputs and Drone Movement
Imagine the sticks as controlling the drone’s movement in three-dimensional space. Forward stick movement results in forward flight (pitch). Right stick movement results in rightward flight (roll). Rotating the right stick controls the yaw (rotation). The left stick’s vertical movement controls the throttle, thus affecting altitude.
Camera Operation and Image Capture
This section details camera settings and controls, offering tips for capturing high-quality aerial photos and videos.
Camera Settings and Controls
Adjusting camera parameters is key to achieving desired image quality. Understanding these settings is essential for professional-looking aerial photography and videography.
- Resolution: Determines the image size and detail. Higher resolutions result in larger file sizes but improved image quality.
- ISO: Measures the camera’s sensitivity to light. Lower ISO values are ideal in bright conditions, while higher ISO values are needed in low light, but can introduce noise.
- Shutter Speed: Controls the length of time the camera’s sensor is exposed to light. Faster shutter speeds freeze motion, while slower speeds create motion blur.
- Aperture: Controls the amount of light entering the camera. A wider aperture (lower f-number) allows more light, resulting in a shallower depth of field.
Tips for High-Quality Aerial Photography and Videography
These tips will help you capture stunning aerial imagery.
- Fly smoothly and avoid sudden movements to prevent blurry images and videos.
- Choose the right time of day for optimal lighting conditions.
- Experiment with different camera angles and perspectives.
- Use a gimbal to stabilize the camera and reduce shake.
- Understand and utilize the camera’s various shooting modes.
Common Camera Modes
Different shooting modes cater to specific creative needs.
- Photo Mode: Captures still images.
- Video Mode: Records moving images.
- Timelapse Mode: Captures a sequence of images over time, which can be compiled into a time-lapse video.
Drone Maintenance and Troubleshooting
Regular maintenance and troubleshooting skills are essential for extending the lifespan of your drone and resolving common issues.
Drone Maintenance Schedule
A regular maintenance schedule will help ensure your drone remains in optimal working condition.
- Weekly: Inspect propellers, motors, and battery for any signs of damage.
- Monthly: Clean the drone body and camera lens.
- Quarterly: Perform a more thorough inspection of all components and connections.
Common Drone Malfunctions and Causes
Understanding common malfunctions and their causes will aid in quicker troubleshooting.
- Low Battery: Insufficient battery charge.
- Motor Failure: Motor damage or ESC malfunction.
- GPS Signal Loss: Obstructions or interference.
- Flight Controller Issues: Software glitches or hardware problems.
Troubleshooting Steps
Effective troubleshooting can resolve many common drone issues.
- Low Battery: Charge the battery fully.
- Motor Failure: Inspect the motor and ESC for damage; replace if necessary.
- GPS Signal Loss: Move to an open area with a clear view of the sky.
- Flight Controller Issues: Try restarting the drone; consider firmware updates or professional repair if necessary.
Understanding and Respecting Regulations
Operating a drone responsibly involves understanding and adhering to local regulations. This section discusses legal requirements and airspace restrictions.
Legal Requirements and Regulations
Drone regulations vary by region. It’s crucial to research and comply with the specific laws in your area before operating a drone.
Many jurisdictions require registration of drones and may have restrictions on where and when you can fly. Some areas may require licenses or permits for commercial drone operations.
Restricted Airspace and No-Fly Zones
Certain areas are restricted for drone flights to ensure safety and security.
- Airports and heliports
- Military bases and installations
- Power plants and critical infrastructure
- Crowded areas and events
- National parks and wildlife reserves (often have specific regulations)
Key Drone Regulations Summary

This table summarizes some key regulations; always check local authorities for the most up-to-date information.
| Regulation Type | Description | Penalty for Violation |
|---|---|---|
| Registration | Many countries require registration of drones above a certain weight. | Fines or legal action |
| Licensing | Commercial drone operation often requires a license. | Fines, operational restrictions, or legal action |
| Airspace Restrictions | Flying near airports or other restricted areas is prohibited. | Fines, operational restrictions, or legal action |
| Privacy | Restrictions may apply regarding the filming or photographing of people without consent. | Fines or legal action |
Advanced Flight Techniques
This section explores advanced flight maneuvers and autonomous flight modes.
Successfully piloting a drone involves understanding its controls and adhering to safety regulations. Learning the basics is crucial before taking flight, and a great resource to help you master this skill is available at how to operate a drone. This comprehensive guide covers everything from pre-flight checks to advanced maneuvers, ensuring you’re prepared to operate a drone safely and effectively.
Advanced Maneuvers

Advanced maneuvers require skill and practice. Always prioritize safety and practice in a controlled environment.
- Waypoint Navigation: Pre-programming a flight path for the drone to follow autonomously.
- Circling: Flying the drone in a circular pattern around a point of interest.
- Following a Subject: Using the drone’s tracking capabilities to follow a moving object.
Autonomous Flight Modes
Many modern drones offer autonomous flight modes, simplifying complex maneuvers and allowing for creative shots.
- Return-to-Home (RTH): The drone automatically returns to its starting point.
- Follow Me: The drone automatically follows the pilot.
- Point of Interest (POI): The drone orbits a specified point.
Planning and Executing Complex Drone Missions
Planning a complex drone mission requires careful consideration of factors like flight path, battery life, airspace restrictions, and weather conditions.
Mission planning software can assist in creating and visualizing complex flight plans. Always conduct thorough pre-flight checks and have a backup plan in case of unforeseen issues.
Mastering the art of drone operation requires a blend of theoretical knowledge and practical application. By understanding the fundamental principles of flight, adhering to safety protocols, and respecting regulatory guidelines, you can unlock a world of creative possibilities. This guide has provided a foundational framework, equipping you with the tools and information necessary to confidently and responsibly operate your drone.
Remember that continuous practice and a commitment to safety are key to becoming a proficient and skilled drone pilot. Safe flying!
Popular Questions: How To Operate A Drone
What type of drone is best for beginners?
Many user-friendly drones with GPS stabilization and automated flight modes are ideal for beginners. Look for models with good crash resistance and easy-to-use controls.
How often should I charge my drone battery?
It’s best to charge your drone battery after each flight and avoid letting it completely discharge. Consult your drone’s manual for specific charging recommendations.
What should I do if my drone loses GPS signal?
Understanding drone operation involves mastering several key skills, from pre-flight checks to navigating airspace regulations. Learning how to control the drone’s movements smoothly and safely is crucial, and a great resource for this is the comprehensive guide on how to operate a drone. This knowledge will enable you to confidently operate your drone, ensuring both successful flights and adherence to safety protocols.
If your drone loses GPS signal, immediately initiate a controlled descent and return to your starting point. Ensure you have a clear view of the drone during this process.
How do I register my drone?
Drone registration requirements vary by region. Check your local aviation authority’s website for specific regulations and registration procedures.
